The Effect of Mofettes on Oxidative Stress/Antioxidant Balance in Experimental Myocardial Ischemia

Asociația Română de Balneologie - Filiala Cluj
Spinal cord injury affects more than 2,5 million people worldwide, with more than 130 000 new injuries reported annually. SCI is the result of aggression on the spinal cord, which totally or partially compromises its functions (motor, sensory, vegetative, reflex). SCI ends in 15% of cases with the victim's death before reaching the hospital. Also, mortality of about. 5% is registered at the level of specialized assistance centers capable of providing qualified, multidisciplinary assistance, while in non-specialized centers the mortality can be between 25-40%. As soon as a severe bonny spine lesion – with affecting the inner content represented by the spinal cord – occurs, the spinal cord usually enters a state of diminished/ abolished excitability, status consisting of altered reflex activity or even spinal shock. Transient inhibition of segments located caudally to the lesion is due to the sudden disappearance of the predominantly facilitating or excitatory influence of supraspinal centers, and at the same time to the local occurring damage mechanisms, thus clinically appearing (tetra-/ para-) paresis and/or flaccid paralysis. The duration of the spinal shock varies, a minimal activity – including with pathological patterns – may emerge within 3-4 days or only after 6-8 weeks (or never), with an average duration of 3-4 weeks, after which there are installed sequelae of the medullary lesion, while remaining local neurons below the lesion level become autonomous to the influences of the upper points. The degree of neurological injury and consequent deficit is determined by the extent and severity of the of above briefly mentioned factors’ action. Pain in patients with SCI dresses almost all possible variants: from acute pain, related to tissue trauma, to colic pain, caused by the presence of lithiasis, respectively to various types of headache, and especially neuropathic pain. The comprehensive, balanced, rehabilitation endeavors and related steps, comprises the application, for prophylactic and curative purposes of a variety of interventions, of: rehabilitation nursing, pharmacological and – very important – of physical/ kinesiological (also balneary – in the chronical stage), types.
In this special issue of Signa Vitae, dedicated to Spinal Cord Injury, we intend to underline general, of intimate level pathological and respectively, treatment mechanisms/ paradigms to undergo the current and future approaches in this domain, and particularly clinical and post research translational aspects, prone to improve the management of this lesions category, to better understand its emergency – including in the chronic/ rehabilitation period – requirements and needs for better practices.

Natural therapeutic factors are widely used as an important adjuvant therapy in various cardiovascular andNatural therapeutic factors are widely used as an important adjuvant therapy in various cardiovascular andcerebrovascular disorders. The aim of this study was to assess the role of balneal therapy on oxidative stressparameters in experimental myocardial ischemia induced in rats. 5 groups of 8 rats were used as follow:group 1- control group; group 2 - group swimming in distilled water (DW); group 3- group with myocardialischemia (MI); group 4 - group with MI swimming in DW; group 5 - group with MI and swimming incarbonated mineral water (CMW). Myocardial ischemia was induced with Isoproterenol. The followingoxidative stress/antioxidant blood parameters were assessed for each animal: nitric oxide (NOx),malondialdechyde (MDA), total oxidative stress (TOS), catalase (CAT) and total ant oxidative capacity ofplasma (TAC). In group 5 all parameters assessed were significantly improved compared with group 3 and4. Carbonated mineral water can be used as an adjuvant therapy for improving oxidative stress/antioxidantstatus in patients with cardiac ischemia, in order to reduce the amplitude of ischemic lesions and tocontribute as a prophylactic therapy to a better quality of life for these patients. Continuing this research inhumans through clinical studies would be warranted.

The main objective of this study was to analyze the perception of the influence of various weather conditions on patients with rheumatic pathology. A group of 394 patients, aged between 39 and 87 years and diagnosed with degenerative rheumatic diseases, were interviewed individually by using a questionnaire created specifically for this study. Further on, to assess the relationship between pain intensity and weather conditions, a frequency analysis based on Pearson’s correlation matrix was employed. The most important results are as follows: the great majority of the participants (more than 75%) believe that their rheumatic pain is definitely or to a great extent influenced by different weather conditions; most of the patients reported intensification of their pain with weather worsening, especially when cloudiness and humidity suddenly increase (83.8% and 82.0%, respectively), air temperature suddenly decreases (81.5%), and in fog or rain conditions (81.2%). In our research, alongside simple meteorological variables, we established that complex weather variables such as atmospheric fronts, in particular, the cold ones and winter anticyclonic conditions, greatly intensify the rheumatic pain, whereas summer anticyclonic conditions usually lead to a decrease in pain severity. In terms of relationships between pain intensity and weather conditions, we found the strongest correlations (ranging between 0.725 and 0.830) when temperature, relative humidity, and cloudiness are constantly high.
Purpose: Anti-inflammatory proprieties of curcumin were proved to be useful in variousPurpose: Anti-inflammatory proprieties of curcumin were proved to be useful in variousdiseases, including diabetes mellitus. The aim of this study was to assess the anti-inflammatorycomparative effect of curcumin solution with liposomal curcumin formula, regarding theimprovement of serum levels of TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-alpha), IL-6 (interleukin),IL-1α, IL-1β, MCP-1 (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1) and RANTES in experimentaldiabetes, induced by streptozotocin (STZ), in rats.
Materials and methods: Six groups of 7 rats were investigated regarding the effect of i.p.(intraperitoneal) administration of two concentrations of curcumin solution (CC1 and CC2) andtwo concentrations of liposomal curcumin (LCC1 and LCC2): group 1 – control group with i.p.administration of 1 mL saline solution, group 2 – i.p. STZ administration (60mg/kg bw, bw=bodyweight), group 3 – STZ+CC1 administration, group 4 – STZ+CC2 administration, group 5 – STZ+ LCC1 administration and group 6 – STZ+ LCC2 administration. The concentrations ofcurcumin formulas were 1 mg/0.1 kg bw for CC1 and LCC1 and 2 mg/0.1 kg bw for CC2 andLCC2, respectively. Serum levels of C-peptide (as an indicator of pancreatic function) andTNF-α, IL-6, IL-1α, IL-1β, MCP-1, and RANTES (as biomarkers for systemic inflammation)were assessed for each group.
Results: The plasma level of C-peptide showed significant improvements when LCC wasadministrated, with better results for LCC2 when compared to LCC1 (P<0.003). LCC2pretreatment proved to be more efficient in reducing the level of TNF-α (P<0.003) andRANTES (P<0.003) than CC2 pretreatment. Upon comparing LCC2 with LCC1 formulas,the differences were significant for TNF-α (P=0.004), IL-1β (P=0.022), and RANTES(P=0.003) levels.
Conclusion: Liposomal curcumin in a dose of 2 mg/0.1 kg bw proved to have an optimumtherapeutic effect as a pretreatment in DM induced by STZ. This result can constitute a basefor clinical studies for curcumin efficiency as adjuvant therapy in type 1 DM.Keywords: diabetes mellitus, inflammation, curcumin, cytokine
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) has been intensively studied for its anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects. Our study aimed to assess the beneficial effect of liposomal EGCG (L-EGCG) co-administered with metoclopramide (MC) on oxidative stress and pain in experimental migraine induced by i.p. nitroglycerine (NG) administration in rats. Five groups of randomly divided rats (7/group) were investigated: control (C, group 1) with i.p. administration of saline solution, NG control group (group 2), NG+MC (group 3), NG+MC+EGCG group (group 4), and NG+MC+L-EGCG (group 5). The nociception was appreciated by the formalin test and the oxidative stress/anti-oxidant status by serum tests. MC alone significantly improved the nociception process and the oxidative stress parameters but not the antioxidative status. Adding EGCG to MC significantly reduced the oxidative stress and antioxidant status together with decreasing of nociception, with better results for L-EGCG.
Arylesterase activity of Paraoxonase 1 - prognostic factorArylesterase activity of Paraoxonase 1 - prognostic factorfor one-year survival in patients with acute myocardial infarction
Lorena Ciumărnean1, Mihai Greavu2, Ştefan C Vesa3, Alina I Tanțău1, Gabriela BDogaru4, Teodora G Alexescu1, Mircea V Milaciu1, George V Saraci5*, Antonia EMacarie6, Ioana Para1
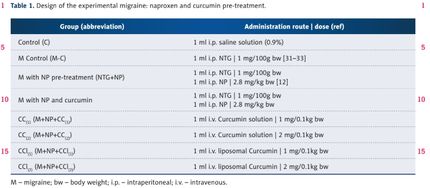
Background: Curcumin is an antioxidant that reduces inflammation and pain. This study aimed to assess the effect of pretreatment with naproxen and liposomal curcumin compared with naproxen and curcumin solution on oxidative stress parameters and pain in a rat model of migraine. Material/Methods: Sixty-three male Wistar rats included a control group (n=9) and a rat model of migraine (n=54) induced by intraperitoneal injection of nitroglycerin (1 mg/0.1 kg). The rat model group was divided into an untreated control group (n=9), a group pretreated with naproxen alone (2.8 mg/kg) (n=9), a group pretreated with naproxen (2.8 mg/kg) combined with curcumin solution (1 mg/0.1 kg) (n=9), a group pretreated with naproxen (2.8 mg/kg) combined with curcumin solution (2 mg/0.1 kg) (n=9), a group pretreated with naproxen (2.8 mg/kg) combined with liposomal curcumin solution (1 mg/0.1 kg) (n=9) a group pretreated with naproxen (2.8 mg/kg) combined with liposomal curcumin solution (2 mg/0.1 kg) (n=9). Spectroscopy measured biomarkers of total oxidative status and nociception was tested using an injection of 1% of formalin into the rat paw. Results: Expression of biomarkers of oxidative stress and enhanced nociception were significantly increased following pretreatment with combined naproxen and liposomal curcumin compared with curcumin solution or naproxen alone (P<0.001). Combined curcumin solution and naproxen were more effective at a concentration of 2 mg/0.1kg for the first nociceptive phase (P<0.005). Conclusions: In a rat model of migraine, combined therapy with liposomal curcumin and naproxen showed an improved antioxidant effect and anti-nociceptive effect.

Adriana Elena Bulboacă 1,Alina S. Porfire 2,Lucia R. Tefas 2,Paul Mihai Boarescu 1,* ,Sorana D. Bolboacă 3,* OrcID,Ioana C. Stănescu 4,Angelo Corneliu Bulboacă 4 andGabriela Dogaru 5
Abstract: Curcumin (CC) is known to have anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties and has already been tested for its efficiency in different diseases including diabetes mellitus (DM). New formulations and route administration were designed to obtain products with higher bioavailability. Our study aimed to test the effect of intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of liposomal curcumin (lCC) as pre-treatment in streptozotocin(STZ)-induced DM in rats on oxidative stress, liver, and pancreatic functional parameters. Forty-two Wistar-Bratislava rats were randomly divided into six groups (seven animals/group): control (no diabetes), control-STZ (STZ-induced DM —60 mg/100g body weight a single dose intraperitoneal administration, and no CC pre-treatment), two groups with DM and CC pre-treatment (1mg/100g bw—STZ + CC1, 2 mg/100g bw—STZ + CC2), and two groups with DM and lCC pre-treatment (1 mg/100g bw—STZ + lCC1, 2 mg/100g bw—STZ + lCC1). Intraperitoneal administration of Curcumin in diabetic rats showed a significant reduction of nitric oxide, malondialdehyde, total oxidative stress, and catalase for both evaluated formulations (CC and lCC) compared to control group (p < 0.005), with higher efficacy of lCC formulation compared to CC solution (p < 0.002, excepting catalase for STZ + CC2vs. STZ + lCC1when p = 0.0845). The CC and lCC showed hepatoprotective and hypoglycemic effects, a decrease in oxidative stress and improvement in anti-oxidative capacity status against STZ-induced DM in rats (p < 0.002). The lCC also proved better efficacy on MMP-2, and -9 plasma levels as compared to CC (p < 0.003, excepting STZ + CC2 vs. STZ + lCC1 comparison with p = 0.0553). The lCC demonstrated significantly better efficacy as compared to curcumin solution on all serum levels of the investigated markers, sustaining its possible use as adjuvant therapy in DM.